Random Variables
|
 |
When modeling a situation where there are n independent trials with a constant probability p of success in each test we use a binomial distribution.
|
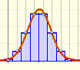 |
In some cases, a Binomial distribution can be approximated by a Normal distribution with the same mean and variance.
|
 |
Poisson distribution is discrete (like the binomial) because the values that can take the random variable are natural numbers, although in the Poisson distribution all the possible cases are theoretically infinite.
|
 |
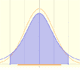
The Normal distribution was studied by Gauss. This is a continuous random variable (the variable can take any real value). The density function is shaped like a bell.
|
 |
One important property of normal distributions is that if we consider intervals centered on the mean and a certain extent proportional to the standard deviation, the probability of these intervals is constant regardless of the mean and standard deviation of the normal distribution considered.
|
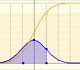 |
The (cumulative) distribution function of a random variable X, evaluated at x, is the probability that X will take a value less than or equal to x. In this page we study the Normal Distribution.
|
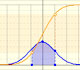 |
Calculating probabilities of symmetric intervals around the mean of a normal distribution.
|
 |
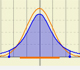
Student's t-distributions were studied by William Gosset(1876-1937) when working with small samples.
|
 |
|
