En esta representación, que también usaremos en las transformaciones de Moebius, sólo se colorean
de color no negro los puntos transformados con módulo pequeño. Es decir, se pierde detalle en el polo.
Podemos elegir dos criterios para elegir el color. En polares los colores se distribuyen en sectores y los tonos
en círculos concéntricos. En cartesianas los colores forman una cuadrícula. Marcando "Identidad" podremos ver
estas dos distribuciones.
En polares, podemos optar por colorear sólo aquellos puntos que se transforman en puntos de módulo menor que 1, aquellos que
están entre 1 y 2 o ambos. Análogamente, en el caso de "cartesianas".
También podemos representar dos bandas: puntos "muy próximos" a 1 y puntos "muy próximos" a 2.
Controlando el exponente del numerador y el del denominador de la función modificamos la multiplicidad
del cero y del polo.
MORE LINKS

Complex power functions with natural exponent have a zero (or root) of multiplicity n in the origin.

A polynomial of degree 2 has two zeros or roots. In this representation you can see Cassini ovals and a lemniscate.

A complex polinomial of degree 3 has three roots or zeros.

Every complex polynomial of degree n has n zeros or roots.

Every complex polynomial of degree n has n zeros or roots.
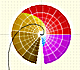
The Complex Exponential Function extends the Real Exponential Function to the complex plane.
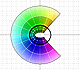
The Complex Cosine Function extends the Real Cosine Function to the complex plane. It is a periodic function that shares several properties with his real ancestor.

The Complex Cosine Function maps horizontal lines to confocal ellipses.
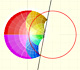
Inversion is a plane transformation that transform straight lines and circles in straight lines and circles.

Inversion preserves the magnitud of angles but the sense is reversed. Orthogonal circles are mapped into orthogonal circles

The usual definition of a function is restrictive. We may broaden the definition of a function to allow f(z) to have many differente values for a single value of z. In this case f is called a many-valued function or a multifunction.
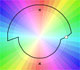
Multifunctions can have more than one branch point. In this page we can see a two-valued multifunction with two branch points.

The complex exponential function is periodic. His power series converges everywhere in the complex plane.

The power series of the Cosine Function converges everywhere in the complex plane.

We will see how Taylor polynomials approximate the function inside its circle of convergence.

 NEXT
NEXT
















 PREVIOUS
PREVIOUS







