The real cosine function can be extended using the exponential function:
As a power series the equivalent definition is:
This series converges everywhere in the complex plane.
If we increase the degree of the Taylor polynomial, this polynomial approaches the function more and more.
We can see it if we look at the Remainder (the difference between the function and the polynomial).
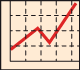
For example, this is a representation of a Taylor's polynomial of degree 5 (In the mathlet we can change the center):
And this is the remainder. We can see how the approximation is much better near the center:
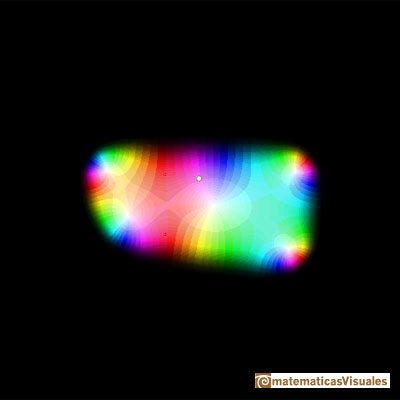
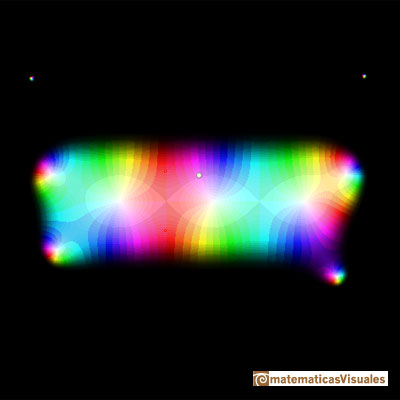
If we increase the degree of the polynomial the approximation is better (degree 10):
The area where the approximation is good is much bigger:
The Cosine Function is periodic with period 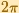 .
.
MORE LINKS

Complex power functions with natural exponent have a zero (or root) of multiplicity n in the origin.

A polynomial of degree 2 has two zeros or roots. In this representation you can see Cassini ovals and a lemniscate.

A complex polinomial of degree 3 has three roots or zeros.

Every complex polynomial of degree n has n zeros or roots.

Every complex polynomial of degree n has n zeros or roots.

Podemos modificar las multiplicidades del cero y del polo de estas funciones sencillas.
The Complex Exponential Function extends the Real Exponential Function to the complex plane.
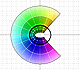
The Complex Cosine Function extends the Real Cosine Function to the complex plane. It is a periodic function that shares several properties with his real ancestor.

The Complex Cosine Function maps horizontal lines to confocal ellipses.

The usual definition of a function is restrictive. We may broaden the definition of a function to allow f(z) to have many differente values for a single value of z. In this case f is called a many-valued function or a multifunction.
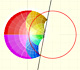
Inversion is a plane transformation that transform straight lines and circles in straight lines and circles.

Inversion preserves the magnitud of angles but the sense is reversed. Orthogonal circles are mapped into orthogonal circles

We will see how Taylor polynomials approximate the function inside its circle of convergence.
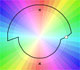
Multifunctions can have more than one branch point. In this page we can see a two-valued multifunction with two branch points.

By increasing the degree, Taylor polynomial approximates the exponential function more and more.
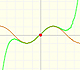
By increasing the degree, Taylor polynomial approximates the sine function more and more.
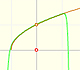
The function is not defined for values less than -1. Taylor polynomials about the origin approximates the function between -1 and 1.

The function has a singularity at -1. Taylor polynomials about the origin approximates the function between -1 and 1.
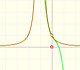
The function has a singularity at -1. Taylor polynomials about the origin approximates the function between -1 and 1.
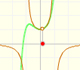
This function has two real singularities at -1 and 1. Taylor polynomials approximate the function in an interval centered at the center of the series. Its radius is the distance to the nearest singularity.

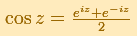

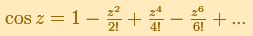


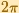 .
.

 PREVIOUS
PREVIOUS