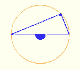
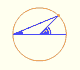
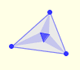
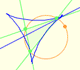
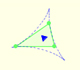
We know that Jacob Steiner (1796-1863) proved that the envelope of the Wallace-Simson lines is a curve that has three cuspidal points that is called the Steiner deltoid.
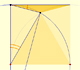
And a deltoid is one specific curve in the family of hypocycloid curves. A hypocycloid is a plane curve generated by the trace of a fixed point on a small circle that rolls without slipping within a larger circle. A deltoid is a hypocycloid in which the inner turning circle has a radius that is one third the radius of the outer circle.
In this page we explore the fact that the Steiner Deltoid is a hypocycloid. It is to say that it is generated by a circle rolling inside another circle.
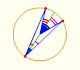
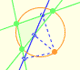
Both circles are related with the Feuerbach circle or the nine-point circle, (green circle in the image). The radius of the nine-point circle is half the radius of the circumscribed circle. The exterior circle has the same center as the nine-point circle and its radius is three times the radius of the nine-point circle.
The rolling circle has the same radius as the Feuerbach circle and both are tangent.
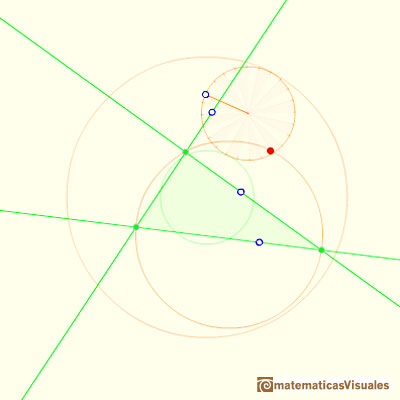
When the small circle rolls without slipping generates the Steiner deltoid.
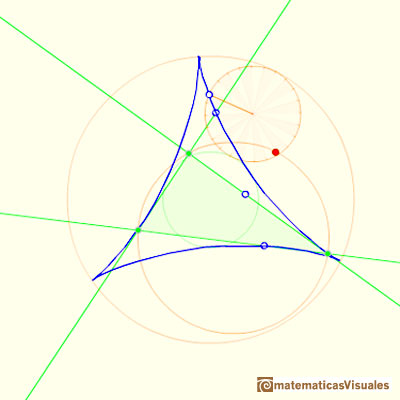
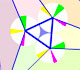
The Steiner deltoid is tangent to the nine-point circle.
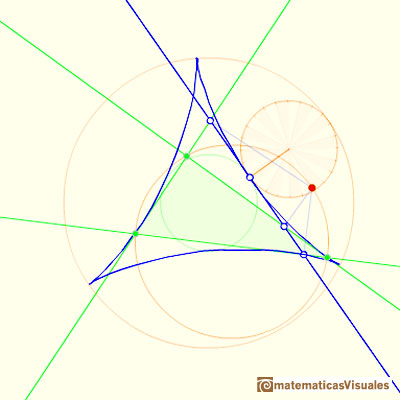
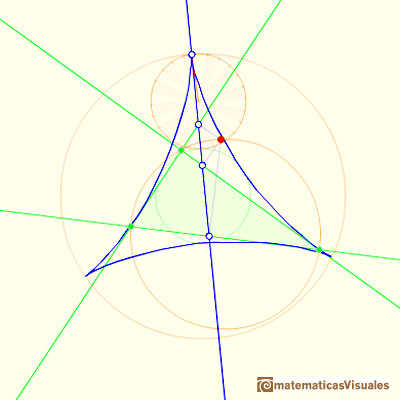
The three tangents to the deltoid at the three cuspides pass through the center of the Feuerbach circle.
REFERENCES
 NEXT
NEXT
 PREVIOUS
PREVIOUS
MORE LINKS